WHAT ARE MACRONUTRIENTS (MACROS)?
Guest Blogger - Sep 24, '19 - Guest Blog
We’re pleased to introduce our guest blogger this week: Tina! Tina Haupert is a Boston-based Lifestyle Influencer & the creative mind behind Carrots 'N' Cake (CNC) - a healthy living blog that helps everyday people achieve more balance via fitness, nutrition, and fun!
WHAT ARE MACRONUTRIENTS (MACROS)?
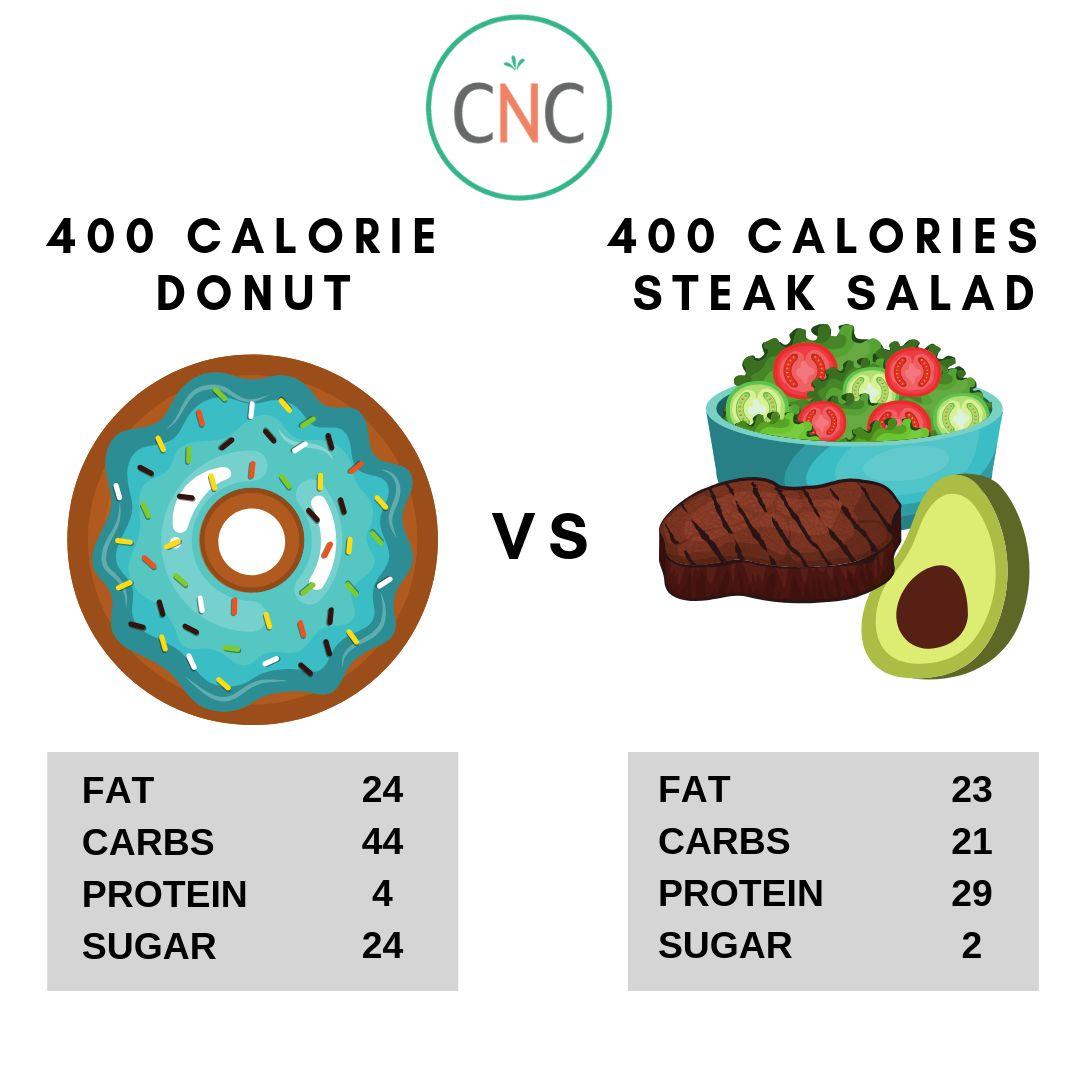
"Macros" are the macronutrients (protein, carbs, and fat) that make up our food. This is where your dietary calories (energy) come from. The ratio of macronutrients that make up the calories in the food you consume determines how satisfied you will be, your energy levels, hormone status, and resulting body composition.
There are three types of macronutrients:
Carbohydrates - provide 4 calories per 1 gram
Protein - provides 4 calories per 1 gram
Fat - provides 9 calories per 1 gram
CARBOHYDRATES
Simply put, carbohydrates provide energy. Quick energy carbs come from fruits, candy, sports drinks, and processed starches, like white bread and crackers. They should be eaten around a workout so your body uses the energy that they provide. When you eat simple carbs and do not use the energy they provide, the excess energy can be stored as fat. Slowly digested, or complex carbs, have more fiber, which prolongs their release of energy and helps to keep digestion regular. Some examples of complex carbs are rolled oats, brown rice, and potatoes. These carbs are ideal when activity isn’t in the immediate future. Non-starchy vegetables, like broccoli, zucchini, and green beans, are also considered carbs, but they contain low amounts of carbohydrate and lots of fiber (important for weight loss), so make sure you get plenty of servings daily!
PROTEIN
Protein is essential for building muscle and repairing damage throughout the body. It is made up of building blocks called amino acids. Some amino acids can be produced in the body and some need to be eaten in food. Your protein intake should depend on your weight and activity. And while getting in enough protein is important—more is not always better. Too much protein, and not enough carbs and fats, can result in the body relying on protein for energy instead of using it for gaining and repair muscle. Knowing your protein needs is key for reaching your weight and activity goals.
FATS
Do NOT fear fat! It’s the types of fat we eat that are important. Fats from plant sources, like nuts, avocados, and vegetable oils are excellent sources. Fats from animals have their place in a healthy diet, too, but should be eaten in lesser amounts since they are higher in saturated fats. When you eat fats is also important. You should try to consume fats in each meal since they will help to keep you fuller longer. Fat shouldn’t be eaten right before or during workouts since your body requires quick energy during those times.
Why are macros important?
Paying attention to the macros in your meals versus just calories helps you create more balanced meals and snacks in your diet. Balanced meals help fight cravings for sugar and junk food and give you sustained energy throughout the day. They also help keep you full and can aid in weight loss as well as weight maintenance.
Just like calories, macros have a big impact on your body composition. For example, if you are not eating enough protein during weight loss, it can lead to a loss of muscle mass instead of fat. Going extremely low carb or low fat with your diet can impact your hormones and metabolism, preventing you from losing weight. Macros can help you find the right balance for your individual dietary needs.
Why should you track macros?
- Helps you find out how much food is appropriate for your activity level
- Helps you find "food freedom" so you can stop feeling guilty about your choices
- Provides you with a framework for your diet instead of feeling like you have no control
- Helps you ditch the idea that restrictive diets are the only way for you to lose weight
- Gets a plan in motion since you have achievable goals to aim for each day
- Keeps you accountable and moving forward with a daily reminder of your goals
- Ready to learn more? Carrots ‘N’ Cake Nutrition and 1-on-1 Coaching is a great way to discover how macros can work for you. With a small staff of Registered Dietitians and nutrition coaches, we provide our clients with personalized attention to help them learn more about their dietary choices, lifestyle habits, and mindset around food to help them reach their goals. Please visit www.cncmacrosplans.com to learn more about our coaching options or reach out directly at [email protected].